Florian ist aufgewachsen auf einem Bauernhof. Umgeben von Pferden, entdeckte er früh seine Faszination für diese majestätischen Tiere. Inspiriert von seiner reitbegeisterten Mutter, entwickelte er das Nahrungsergänzungmittel - Pferdegold. Seine tiefe Verbundenheit zur Natur und die leidenschaftliche Hingabe zu Pferden trieben ihn an, sein Unternehmen zu gründen.
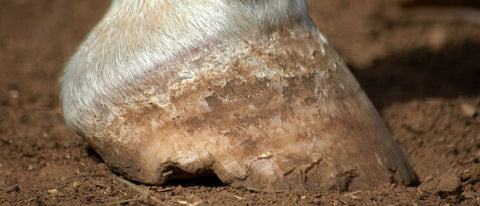
Imagine you're standing in the stable, picking out your horse's hooves, and suddenly you notice signs that make you suspicious. Could it be laminitis?
This painful hoof disease can affect any horse and requires attention and swift action. Laminitis poses a serious threat to the health of horses.
In this guide, we will show you how to recognize laminitis, what treatment options are available, and what you can do to prevent it in the first place.
We will also explain in detail what laminitis is, how it develops, and how you can best support your horse.
With the right knowledge and action, you can help ensure your horse receives careful and competent care and prevent laminitis.

What exactly is laminitis in horses?
Laminitis is a serious hoof disease in horses characterized by inflammation of the hoof capsule .
This inflammation causes considerable pain and can severely impair the horse's mobility.
Laminitis occurs when the connection between the hoof and bone is disrupted , which can cause a variety of problems.
It is important to recognize the signs of laminitis early so that your horse can be helped in time.
Causes of laminitis: What factors are responsible?
Various factors can trigger this painful condition.
It is important to know these causes in order to prevent laminitis.
1. Stress-induced laminitis
Stress-induced laminitis occurs when a horse distributes its weight unevenly across its hooves .
This can be caused by injuries, long periods of standing on hard surfaces or extreme physical exertion.
The uneven load leads to an overstrain of the hoof capsule, which can result in inflammation and thus laminitis.
2. Feeding deer
Laminitis is a form of laminitis caused by an inadequate diet .
Too much grain, sudden grazing on lush grass, or too many carbohydrates can put a strain on the horse's digestive system and lead to laminitis.
A balanced diet is therefore essential to avoid deer fodder.
3. Poisoned deer
Poisoning occurs when deer are ingested with toxic substances . This can occur through contaminated feed, poisonous plants, or medications .
The toxins damage the blood vessels in the hoof, which can lead to inflammation and laminitis.
4. Lyme disease
Lyme disease, a tick-borne disease , can also cause laminitis. The infection impairs the horse's immune system and can lead to an inflammatory reaction in the hooves.
5. Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome, a hormonal disorder , is another cause of laminitis. This condition, also known as equine Cushing's syndrome , leads to an overproduction of cortisol in the horse's body .
This significantly impairs the horse's metabolism and increases the risk of laminitis.
Horses with Cushing's syndrome often show an increased susceptibility to various diseases, including laminitis, and therefore require careful monitoring and special care to maintain their health.
6. Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS)
EMS is a metabolic disease that leads to obesity and insulin resistance . These factors significantly increase the risk of laminitis.
Horses with EMS are particularly susceptible to laminitis because their bodies are less able to process carbohydrates.
An appropriate diet and regular exercise are crucial to minimize the risk of laminitis in horses with EMS .
7. Obesity
Obesity places excessive strain on a horse's hooves and can lead to laminitis. Excessive weight gain, often caused by an overly rich diet and lack of exercise , increases pressure on the hoof structures .
A balanced diet and regular exercise are important to prevent obesity and the associated laminitis.

Horse owners should look out for these symptoms in laminitis
Laminitis is a serious condition in horses that must be detected early to avoid serious consequences. It is important to recognize the symptoms at their different stages to intervene promptly.
➽ Symptoms in Phase 1 (Early Stage): The early signs of laminitis in horses often present with nonspecific symptoms . They may exhibit mild lameness or reluctance to walk .
Increased pulsation in the hoof arteries may also occur . This stage is often overlooked because the insidious symptoms of early laminitis are subtle and easy to miss.
➽ Symptoms in Phase 2: In this phase, the laminitis symptoms become more pronounced . The horse exhibits more severe lameness, especially when walking on hard surfaces. The hooves often feel warm, and the horse may exhibit pain when pressure is applied to the sole. This is a critical time to recognize laminitis and initiate appropriate treatment promptly.
➽ Symptoms in Phase 3: In the third phase of laminitis, symptoms continue to worsen . The horse now exhibits significant pain reactions and may refuse to move.
The hooves are extremely sensitive , and changes in the hoof structure can occur. During this phase, the symptoms of laminitis in horses are obvious and require immediate veterinary attention .
➽ Symptoms in Phase 4 (End Stage): In the end stage of laminitis, the damage to the hoof is often irreversible. The horse suffers extreme pain , and complete separation of the hoof capsule may occur.
At this stage, the prognosis is often poor, and the goal is to minimize the animal's suffering.
As a horse owner , it's crucial for you to be alert and attentive to the first signs of laminitis . Early detection and intervention can be vital to stopping the progression of this serious condition. With a prompt diagnosis and proper treatment, you can not only preserve your horse's health but also ensure its overall well-being in the long term.
Therefore, always pay attention to the smallest symptoms – with laminitis, every minute counts .

How is laminitis diagnosed?
Diagnosing laminitis always requires a thorough examination by a veterinarian . First, the veterinarian will perform a clinical examination of your horse, paying particular attention to its hooves and gait.
The hooves are checked for warmth, pulsation, and pain response . A detailed medical history is taken, including an examination of feeding habits, previous illnesses, and the horse's behavior.
Imaging techniques such as x-rays can be used to assess the extent of damage to the hoof and to determine whether there has been any displacement of the coffin bone.
In some cases, blood tests may also be performed to identify possible underlying metabolic disorders or inflammatory processes.
Laminitis treatment: What really helps?
When treating laminitis, it is crucial to act quickly and effectively. Laminitis treatment often includes a combination of drug therapy, dietary adjustments, and specialized hoof care .
When treating laminitis, it is important to identify the cause and address it specifically. Hoof inflammation in horses often requires anti-inflammatory medication and rest.
In chronic laminitis, long-term treatment with regular monitoring and adjustment of hoof care is essential.
It is important that you work closely with your veterinarian and farrier to find the best laminitis treatment for your horse.
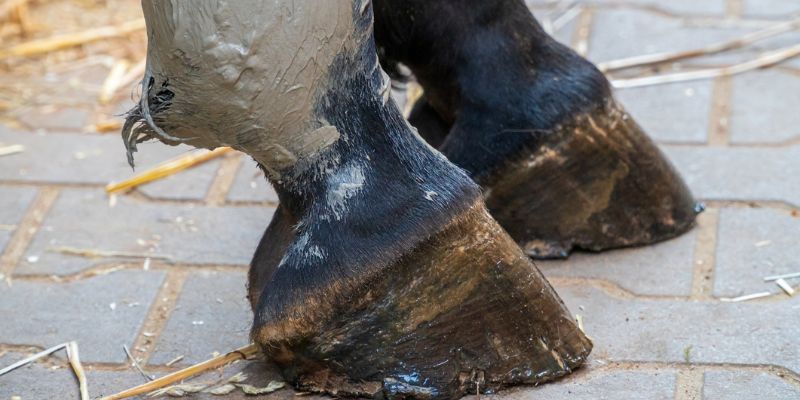

Deer casts
Laminitis casts are an important part of laminitis treatment.
They support healing by stabilizing the hoof and relieving pressure.
-
The lower laminitis cast: This cast covers the lower part of the hoof and helps support the hoof structure. It is often used to minimize stress on the inflamed area and relieve pain.
-
The medium laminitis cast: This cast covers the middle of the hoof. It provides additional support and helps maintain correct hoof alignment, which is crucial for healing.
- The high laminitis cast: The high laminitis cast extends beyond the coronary band. It offers maximum stability and is particularly important in severe cases of laminitis.
How can a farrier help with treatment?
An experienced farrier is essential in the treatment of laminitis. They can make special shoes that reduce pressure on the inflamed area and assist the horse in walking.
Through regular hoof care and adjustments to the shoes, the farrier can help improve the hoof structure and prevent further damage.
He can also provide valuable tips on the care and hoof management of the horse to prevent a recurrence of laminitis.

Perfect for your horse: Pferdegold® supplementary feed!
These specially developed supplements support your horse's diet and provide it with natural nutrients. Made in Germany, grain-free and drug-free, with a 30-day money-back guarantee.
Try it now!15 tips that really help: How to prevent laminitis
Prevention of laminitis begins with a comprehensive understanding of the disease and careful care.
Here are 15 tips that can help you prevent laminitis :
-
Balanced diet: Make sure you eat a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients and low in sugar.
-
Regular exercise: Ensure your horse gets regular exercise. This not only promotes overall health and fitness, but also supports blood circulation in the hooves and can thus help prevent hoof problems.
-
Weight management: Monitor your horse's weight to avoid obesity. Obesity is a known risk factor for laminitis and can place additional stress on the hooves.
-
Regular hoof care: Keep your horse's hooves in good condition through regular care and inspections by a farrier.
-
Avoiding stress: Try to minimize stressful situations for your horse, as stress can be a trigger for laminitis.
-
Caution when grazing: Be especially careful with fresh grass, especially in spring and autumn, as it can have a high sugar content.
-
Water access: Make sure your horse always has access to fresh, clean water.
-
Regular veterinary check-ups: Have your horse examined by a veterinarian regularly to detect health problems early.
-
Adjusting feeding: Adjust feeding to your horse's needs and activity level.
-
Monitoring medication administration: Be careful when administering medications that can trigger laminitis.
-
Avoid overloading: Avoid excessive strain on the hooves due to overly hard training or poor ground conditions.
-
Early detection of symptoms: Learn to recognize the signs of laminitis so you can act quickly.
-
Good stable hygiene: Keep the stable clean and dry to avoid hoof problems.
-
Communicate with experts: Communicate regularly with your veterinarian and farrier to ensure the best management for your horse.
-
Education and information: Stay informed about the latest findings and treatments for laminitis.
By following these tips, you can help reduce the risk of laminitis in your horse and promote his long-term well-being.

First aid for laminitis: What horse owners should definitely do
If you suspect your horse is suffering from laminitis, you need to act quickly . First, you should contact a veterinarian immediately.
Until the veterinarian arrives, there are some steps you can take to help your horse. Avoid moving your horse, as this can worsen the pain .
Place your horse on soft ground, such as sand or sawdust, to minimize pressure on the hooves.
Cooling can also help reduce inflammation .
It is also important to prevent access to food, especially fresh grass, as this can worsen the symptoms.
Remember that these measures are only temporary and professional treatment by a veterinarian is essential.
Is laminitis curable? All about the chances of recovery
The question of whether laminitis is curable concerns many horse owners .
Here is the good news : The chances of recovery are often good , especially if the disease is detected early and treated quickly.
In the early stages of laminitis, you can achieve a lot by acting quickly and correctly.
However, the healing time varies and depends on various factors , such as the general health of your horse and the severity of the disease.
Unfortunately, in some cases, laminitis can cause long-lasting damage that requires ongoing care and careful management .
A complete cure may not be possible in such cases, but with the right treatment you can significantly improve your horse's quality of life .
Remember that close cooperation with your veterinarian and farrier is crucial to achieve the best results.
Conclusion
In summary, laminitis is a challenge, but one that can be managed with knowledge, awareness, and commitment. Your horse relies on your care and understanding.
By recognizing the signs early, reacting appropriately, and taking preventative measures, you can support your horse in everything.
Remember that every step you take, whether it's regular hoof care, careful weight monitoring, or even a balanced diet, can make a difference.
At Pferdegold, we want to do everything we can to provide you with the best possible support when it comes to feeding your horse.
IMPORTANT:
Horse gold replaced not a veterinary diagnosis or treatment . The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only and is intended to help improve your horse's well-being.
Pferdegold products They do not treat or cure diseases , but rather support your horse in correcting nutritional deficiencies through targeted nutrient intake. However, they are not a substitute for professional advice from a veterinarian or specialist.
If your horse has any health problems, we strongly recommend consulting a veterinarian. Pferdegold assumes no liability for decisions made based on the information provided here.
FAQ
What shouldn't a horse with laminitis eat?
Horses with laminitis should avoid certain feeds to avoid aggravating the situation. Avoid carbohydrate-rich feeds such as grains and fresh grass, especially in spring when sugar levels are high.
Treats and fruit should also be given in moderation. Instead, opt for high-quality hay and special diets low in starch and sugar.
Is exercise good for laminitis?
Exercise is a double-edged sword when it comes to laminitis. On the one hand, light exercise can promote blood circulation and help control weight, which is important for recovery.
On the other hand, too much exercise can put strain on the hooves and cause pain.
It is important to work with your veterinarian to create an individual exercise plan that is tailored to your horse's condition and needs.
What happens if laminitis is not treated?
Failure to treat laminitis can have serious consequences. The disease can progress and lead to permanent damage to the hoof, resulting in severe pain and lameness.
It is therefore important to act immediately at the first signs of laminitis and seek professional help.
🐎 Want to learn more about horses and their health? Read on: